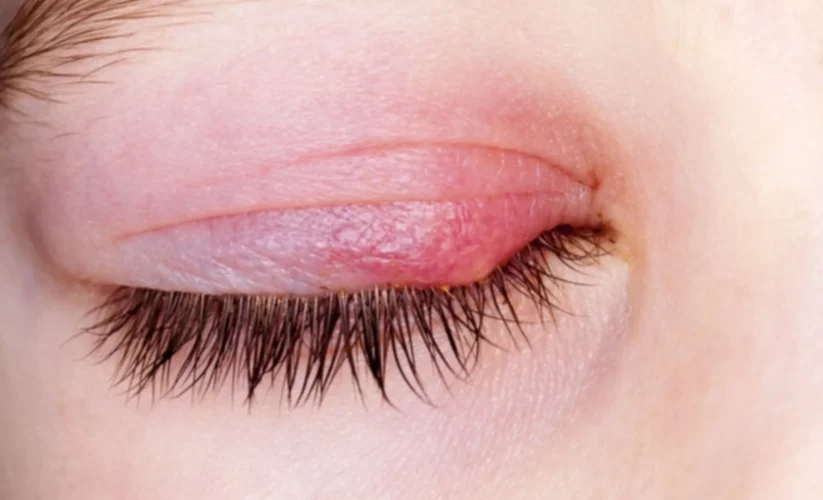
Commonly Misdiagnosed Conditions Mistaken for Pink Eye
Pink eye, or conjunctivitis, is a common eye condition characterized by inflammation of the conjunctiva, the thin, transparent layer that covers the white part of the eye and lines the inner surface of the eyelids. While pink eye is often the first assumption when someone experiences redness, itching, and irritation in the eye, what is commonly misdiagnosed as pink eye? Several other conditions can mimic its symptoms. Misdiagnosis can lead to inappropriate treatment and prolonged discomfort.
What is commonly misdiagnosed as pink eye?
Here are some reasons for being misdiagnosed with pink eye:
Allergic Conjunctivitis
Differentiation: Allergic conjunctivitis usually accompanies other allergic symptoms such as sneezing, nasal congestion, and itchy throat. Additionally, symptoms may be seasonal or occur in response to specific triggers.
Dry Eye Syndrome
Dry eye syndrome occurs when the eyes do not produce enough tears or when tears evaporate too quickly. This can lead to redness, irritation, a burning sensation, and a gritty eye feeling. In some cases, dry eye syndrome can be mistaken for pink eye, especially if redness and irritation are the primary symptoms.
Differentiation: Dry eye syndrome is often exacerbated by prolonged screen time, environmental conditions (e.g., wind, smoke), and wearing contact lenses. What is commonly misdiagnosed as pink eye? This question prompts consideration of alternative diagnoses. Symptoms of dry eye syndrome may improve with the use of artificial tears or prescription eye drops.
Blepharitis
Blepharitis is a common condition characterized by inflammation of the eyelids, typically at the base of the eyelashes. It can result in symptoms such as redness, itching, burning, and crusting of the eyelids. In some cases, the inflammation may spread to the conjunctiva, causing symptoms similar to those of pink eye.
Differentiation: Unlike the pink eye, blepharitis primarily affects the eyelids rather than the conjunctiva. Patients with blepharitis may also experience dandruff-like flakes on the eyelashes and a sensation of something in the eye.
Corneal Abrasion
A corneal abrasion is a scratch or injury to the cornea, the clear, dome-shaped surface that covers the front of the eye. Common causes include foreign objects, contact lens wear, and eye trauma. Symptoms of corneal abrasion may include redness, tearing, pain, sensitivity to light, and a feeling of something in the eye.
Differentiation: While pink eye primarily affects the conjunctiva, a corneal abrasion damages the cornea. Patients with corneal abrasions often report localized pain and discomfort, particularly when blinking or looking at light.
Subconjunctival Hemorrhage
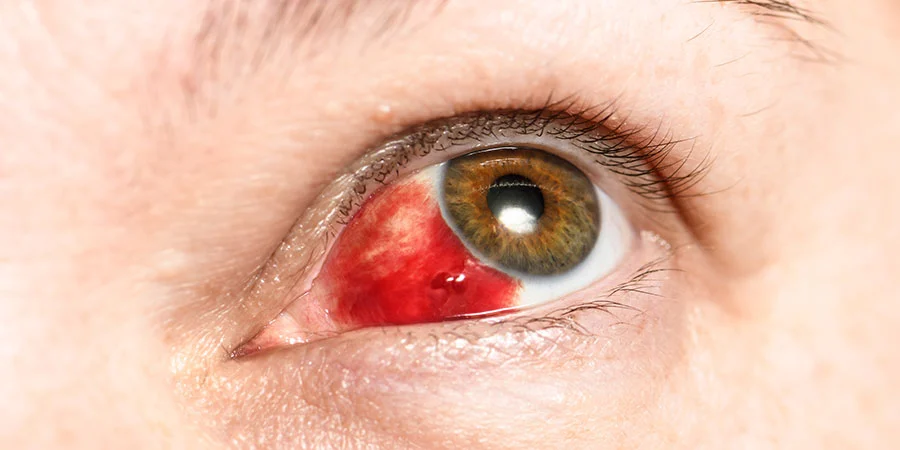
A subconjunctival haemorrhage occurs when a small blood vessel breaks open beneath the conjunctiva, causing a red patch to appear on the white of the eye. This can be alarming and may resemble the redness associated with pink eye. Subconjunctival haemorrhages are typically painless and resolve independently within a few weeks.
Differentiation: Unlike pink eye, subconjunctival haemorrhages do not cause itching, discharge, or crusting of the eyelids. They are often asymptomatic and may be noticed incidentally or following activities that increase intraocular pressure, such as coughing or straining. What is commonly misdiagnosed as pink eye? Although alarming in appearance, subconjunctival haemorrhages are typically harmless and resolve independently without treatment.
Viral or Bacterial Keratitis
Keratitis is inflammation of the cornea, which viral or bacterial infections and other factors such as trauma or contact lens wear can cause. Symptoms may include redness, pain, blurred vision, light sensitivity, and eye discharge. Sometimes, the initial viral or bacterial keratitis presentation may be mistaken for pink eye.
Differentiation: Unlike pink eye, keratitis often involves more severe symptoms such as intense pain, photophobia, and decreased vision. Prompt diagnosis and treatment are essential to prevent complications such as corneal scarring and vision loss. What is commonly misdiagnosed as pink eye? Conditions such as uveitis or viral keratitis share similar symptoms with pink eye but require different management strategies. By recognizing these distinctions, healthcare providers can ensure accurate diagnoses and appropriate treatment plans, thereby minimizing the risk of complications and optimizing patient outcomes.
Contact Dermatitis
Contact Dermatitis of the eye occurs when the conjunctiva becomes irritated or inflamed in response to contact with allergens or irritants such as cosmetics, eye drops, or contact lens solutions. Symptoms may include redness, itching, swelling, and a burning sensation in the eyes. In some cases, the presentation of contact dermatitis can mimic that of pink eye, leading to potential misdiagnosis.
Differentiation: Contact dermatitis typically affects only the areas of the eye that come into contact with the allergen or irritant. Patients may report a history of recent exposure to a new product or substance, which can help differentiate it from infectious conjunctivitis.
Uveitis
Uveitis is inflammation of the uvea, the middle layer of the eye, including the iris, ciliary body, and choroid. Infections, autoimmune disorders, or other underlying conditions can cause it. Symptoms of uveitis may include eye redness, pain, blurred vision, sensitivity to light, and floaters. In some cases, uveitis may be mistaken for pink eye, especially if the inflammation involves the conjunctiva.
Differentiation: Unlike the pink eye, uveitis often presents with more severe symptoms and may be associated with systemic manifestations such as joint pain, fever, or skin rash. Examination by an ophthalmologist is crucial for accurate diagnosis and appropriate management of uveitis.
Conclusion
While pink eye is a common and relatively benign condition, healthcare providers must consider other potential causes of eye redness and irritation when evaluating patients. Misdiagnosis can lead to unnecessary treatment, delays in appropriate management, and possible complications. By understanding the distinguishing features of conditions commonly mistaken for pink eye, clinicians can make accurate diagnoses and provide optimal patient care. What is commonly misdiagnosed as pink eye? This question prompts healthcare providers to delve deeper into the differential diagnosis and consider alternative conditions presenting with similar symptoms.
Additionally, prompt referral to an ophthalmologist may be necessary in cases where the diagnosis is uncertain or when more serious underlying conditions are suspected. Through thorough assessment and appropriate management, healthcare providers can ensure the best possible outcomes for individuals with eye symptoms.





